Adnexal masses present a special diagnostic challenge in part because benign adnexal masses greatly outnumber malignant ones. Endovaginal ultrasonography US is the most practical modality for assessment of ovarian tumors because it is readily available and.
Benign And Malignant Characteristics Of Breast Lesions At Ultrasound Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
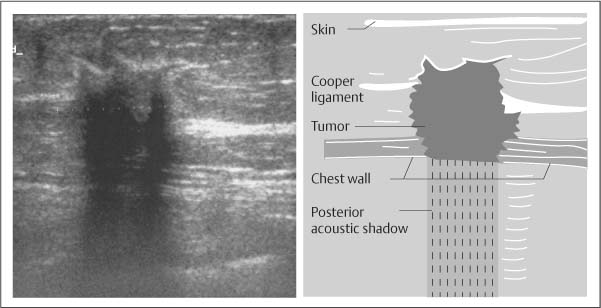
Appropriate compression and angulation of the transducer can eliminate posterior acoustic shadowing allowing an anatomic structure to be easily recognized as normal on real-time US.

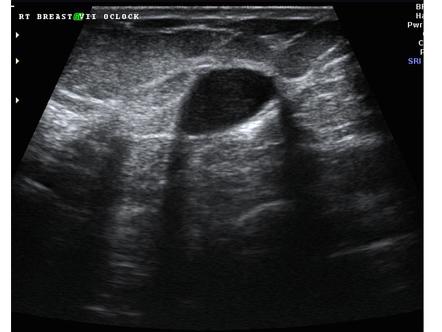
. To the right side of the image near the gallbladder fundus there is also shadowing but no evidence of stones. The phenomenon of acoustic shadowing sometimes somewhat tautologically called posterior acoustic shadowing on an ultrasound image is characterized by a signal void behind structures that strongly absorb or reflect ultrasonic wavesIt is a form of imaging artifactThis happens most frequently with solid structures as sound conducts most rapidly in. However posterior acoustic shadowing caused by a desmoplastic reaction can be found in benign breast neoplasms as well.
A fat lobule is occasionally seen as an isoechoic. The above ultrasound images of the right kidney show echogenic debris layering at the dependent part of a small cyst. Determination of a degree of suspicion for malignancy is critical and is based largely on imaging appearance.
The first shows a large gallstone with posterior shadowing that is possibly impacted in the gallbladder neck. For example fibrosis inside a tumor can block ultrasound from passing deeper causing acoustic shadowing. The echogenic hilus is mainly the result of multiple medullary sinuses which act as acoustic interfaces and partially reflect the ultrasound waves to produce an echogenic structure.
Often might not actually represent calcifications 6 most specific finding associated with. Although calcification can be seen in both benign and malignant processes it is the ultrasound feature most closely associated with malignancy 1. Punctate echogenic foci without posterior shadowing.
In the normal neck about 90 of nodes with a maximum transverse diameter greater than 5 mm will demonstrate an echogenic hilus on high resolution ultrasound 43. There is change in the fluid-debris interphase with change in position. In ACR TI-RADS points in five feature categories are summed to.
These are typical findings of Milk of Calcium within a renal cyst. In 2017 the Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System TI-RADS Committee of the American College of Radiology ACR published a white paper that presented a new risk-stratification system for classifying thyroid nodules on the basis of their appearance at ultrasonography US. There is minimal acoustic shadowing due to a relatively large amount of calcium debris.
This could be due to an air collection from gallbladder rupture see labeled ultrasound below.

Sonographic Evaluation Of Benign And Malignant Breast Masses Iame

Ultrasound Image Of A Breast Cancer With Irregular Borders Angular Download Scientific Diagram

Transverse Ultrasound Of The Left Breast Demonstrates An Irregular Download Scientific Diagram
Basic Principles Radiology Key

Posterior Acoustic Shadowing In Benign Breast Lesions Weinstein 2004 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library

Posterior Acoustic Shadowing In Benign Breast Lesions Weinstein 2004 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
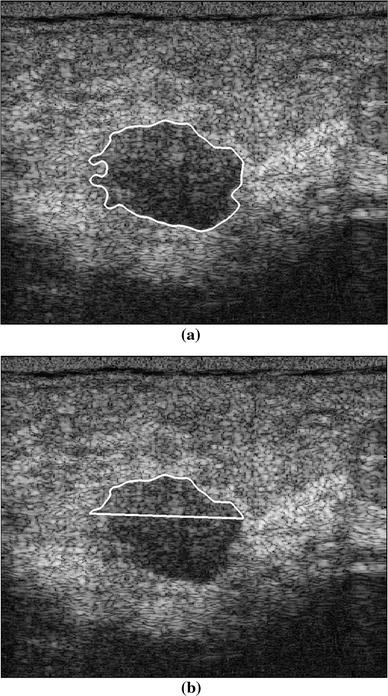
Classification Of Benign And Malignant Breast Tumors In Ultrasound Images With Posterior Acoustic Shadowing Using Half Contour Features Springerlink

The Relationship Between Lateral Acoustic Shadow Feature On Ultrasound Download Scientific Diagram
0 komentar
Posting Komentar